Retail business intelligence (BI) is a powerful tool for modern retailers to stay ahead of the curve and deliver value. It can help you improve sales in-store, customer experience, and inventory management.
Retail BI is changing the game by making analytics and business intelligence more accessible, accurate, and affordable for retailers of all sizes. Retailers can now make better decisions based on data-driven insights for increased foot traffic and sales.
What is retail business intelligence?

Retail business intelligence is the automated process of turning data into actionable insights by collecting, cleaning, and analyzing the data. It is also referred to as retail BI.
There are many processes and tools retailers can use to receive relevant insights, including:
- Data analytics
- Predictive insights from artificial intelligence (AI)
- Data visualizations
- Psychographic and demographic data
All aspects of business intelligence have benefits for retail businesses, but how much and how you should use it varies depending on your business type. Get the most out of retail BI by identifying key problem areas, tracking performance, and using the right data for the right job.
Advantages of business intelligence in the retail industry
Without big data analytics, companies are blind and deaf, wandering out onto the web like deer on a freeway.
– Geoffrey Moore
When Moore, a management Consultant and theorist, tweeted this back in 2012, some perceived it as hyperbolic. In retrospect, we can safely say Moore had it right.
Retail BI essentially combines data from across your operations and the wider market, crunches the numbers, and delivers actionable insights straight to your dashboard.

Not convinced? Here are the key advantages:
- Improve stock management
- Boost marketing campaigns
- Understand your customers
- Improve customer retention
- Track social media metrics
1. Improve stock management

Identify which products are trending up and which ones are decreasing to decide how to price certain products, offer products at a discount, and better prepare stock.
A study by McKinsey found that technology such as retail advanced analytics can help stores by reducing shrinkage by up to 20%.
2. Boost marketing campaigns
Which marketing campaigns are driving traffic to your store? How are you measuring success? Optimize your marketing using data.
See our case study with Clear Channel, where we maximized offline Out-of-Home (OOH) measurability to optimize real-world ad campaigns.
3. Understand your customers
Identify high-value customers, target campaigns, and understand their needs. Retail BI providers can now offer detailed, aggregated raw data, reports, and insights on store visitors. This data is collected and analyzed while respecting privacy.
Greater customer understanding can help you build optimized marketing campaigns, adjust store hours, and prepare stock.
4. Improve customer retention
Retail BI tools and strategies can increase customer retention by providing an in-depth analysis of customer interactions, demographics, and psychographics. Analysis from BI is then used to produce higher-quality strategies that engage customers, improving conversion rates and retention.
5. Track social media metrics
Social media is king in the online world and everyone from brick-and-mortar retailers to malls and offices can hugely benefit from it. There are many ways to track social media metrics, including in the social media app or website.
However, using a social media management tool such as Hubspot or Hootsuite can provide insights on all social media accounts in one platform to save time.
It’s not just your own social media metrics you need to be tracking. Your competitors are also posting. So see how they’re doing, how often they post, what they post, who responds, and if you can learn from their strategies.
6. See where your customers shop
What stores are your customers visiting other than yours? Visitor cross-shopping is an important metric that tells you the other locations your customers have visited within the past year. Think of it as a “customers who also bought this liked…” but in retail company form.
If there’s a high percentage of cross-over, you could have discovered a direct competitor. Some companies, those who are not your direct competitors, can make excellent partners as you now know from the cross-shopping data that your customers have similar interests.
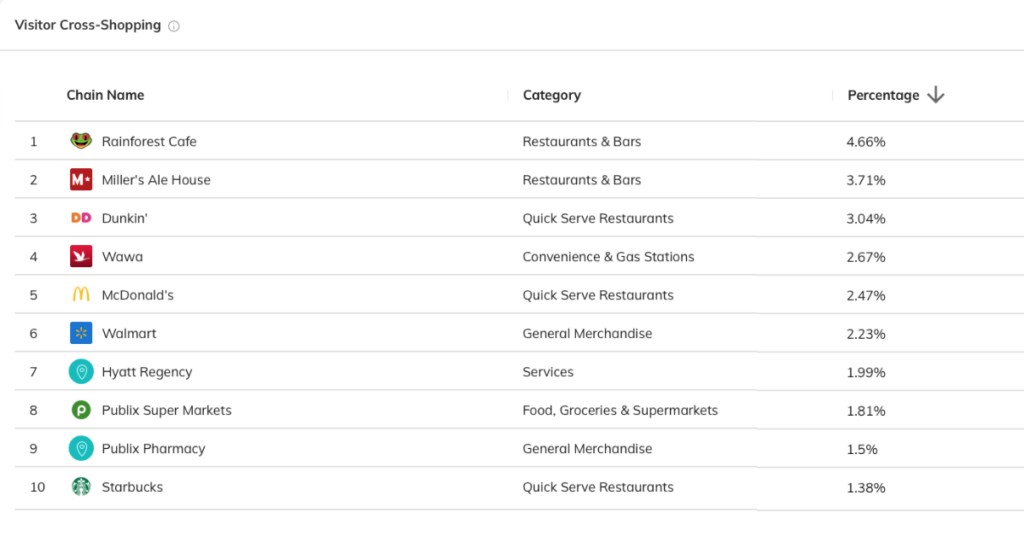
Get visitor cross-shopping data for retail business intelligence on Almanac.
How businesses are driving success through retail BI
In the constantly transforming retail industry, the significance of data cannot be overstated. With unprecedented competition and sky-high customer expectations, staying ahead of the curve requires more than just intuition; it requiresbusiness Intelligence.
The power of predictive analytics
When it comes to retail business intelligence, one tool stands out among the rest – predictive analytics.
As the name suggests, this tool is designed to forecast trends, customer behaviors, and potential sales opportunities. It’s not just about understanding what’s happening now in your retail business—it’s about predicting what could happen in the future and preparing for these events.
Predictive analytics can help you in many ways. For example, by setting a benchmark of foot traffic based on your competitors, area, and previous performance.

Reach the right customers
Retailers can use dashboards on data intelligence platforms to see an overview and insights into performance details. These platforms can track many types of data including consumer mobility events and footfall data.
By checking this data, analyzing it, and implementing the platform’s insights, retailers can improve their understanding of consumer behavior. This can look like altering product placements, adjusting store hours for customer convenience and performance, and targetting local customers for higher engagement marketing campaigns.
Retail business intelligence examples from the industry
Are there businesses in your sphere leveraging the power of business intelligence? The answer is a resounding yes! Market leaders have been using retail BI for years to get and stay ahead of the rest.
Here we take a look at some companies that have integrated business intelligence into their operations.
Nike
In 2019, Nike acquired Celect, the Boston-based predictive analytics company.
Some of the main goals were to reduce out-of-stock rates and improve sales directly to customers, reducing the reliance on wholesalers.
That isn’t the only acquisition Nike has made to improve its data analytics toolset.
Sephora
The beauty retailer Sephora was an early adopter of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, using it as early as 2013.
Since then, the company has used retail BI and machine learning to limit the differences between online and offline shopping experiences.
Walmart
Walmart is one of the largest retail companies in the United States and it is a market leader for using retail BI at its in-house data research and technology development organization within Walmart.
Walmart uses business intelligence in many ways including analyzing purchase patterns: Which products are commonly bought together? Tracking these purchases enables Walmart to place these products nearby, bundle in a deal, or recommend them on website’s online shopping cart.
See our case studies and discover how companies are using retail business intelligence to optimize their operations.
Future Trends in Retail Business Intelligence: What to Expect
The future of retail BI is bright, as companies are increasingly recognizing the value of data-driven decision-making. You can expect to see the following trends:
- Increased use AI: AI can be used to automate many of the tasks involved in BI, such as data collection, cleaning, and analysis. This will free up analysts to focus on more strategic tasks, such as developing and deploying new insights.
- Real-time analytics: Retailers can use real-time analytics to make decisions based on the latest data, rather than having to wait for reports to be generated. This is becoming increasingly important in the fast-paced industry.
- More focus on predictive analytics: Predictions should be used to forecast future demand, predict customer churn, and identify other trends. This information can be used to make better decisions about inventory, pricing, and marketing.
- Omnichannel analytics: Consumers are spread across channels, including online, in-store, and mobile apps. Tracking these different channels all-in-one is more than important than ever to ensure a seamless customer experience.
Retailers that want to power ahead of the competition need to implement efficient retail BI now or risk falling behind, losing sales, and lagging in customer satisfaction. The potential gains for using business intelligence are higher than ever as the goalposts continue to shift in an increasingly digital shopping economy.
To see how data could help your retail store, speak to our team.
Retail business intelligence FAQs
What is another name for business intelligence?
Retail business intelligence is often shortened to retail BI or simply BI. It may also be referred to as a decision support system.
What is a retail intelligence platform?
A retail intelligence platform is a tool, either software or an online portal, that works to support retail companies in collecting, tracking, cleaning, processing, analyzing, and visualizing data. These platforms can offer further insights into the data, trends, and consumer behavior through highly-trained machine learning (ML) models.
How can AI improve retail?
In retail business intelligence, AI can be used for predictive analytics. The AI takes a large data set, such as the past five years of a store’s past performance, and can then output predictions on future performance. Predictive analytics of up to 3 months for retail is available from Almanac by pass_by, a reporting tool that offers unprecedented insight.
How do companies use business intelligence?
Companies use business intelligence (BI) tools and platforms to build strategies, support decision-making, and present data. Companies use BI to create trend analysis, identify competitors, and analyze past performance.


